Navigation für Produktinformationen
Struktur von Melanotan-I
- Sequenz:Ser-Tyr-Ser-Nle-Glu-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly-Lys-Pro-Val
- CAS-Nummer:C78H111N21O19
- Molekulare Formel:1646.874 g/mol
- Molekulargewicht: 75921-69-6
Was ist Melanotan-I?
Melanotan 1 ist ein synthetisches Analogon des alpha-Melanozyten-stimulierenden Hormons. Es wird in Europa klinisch eingesetzt, um sonnenbedingte Hautschäden (d. h. Phototoxizität) bei Patienten mit erythropoetischer Protoporphyrie zu verhindern. Obwohl Melanotan 1 ursprünglich als sonnenloses Bräunungsmittel entwickelt wurde, hat man festgestellt, dass es eine Reihe physiologischer Wirkungen auf den Blutdruck, das Fressverhalten und die Funktion des zentralen Nervensystems hat. Das Peptid befindet sich in klinischen Studien der Phase 3 zur Behandlung von polymorphem Sonnenausschlag und in klinischen Studien der Phase 2 zur Behandlung von aktinischer Keratose, einer speziellen Art von sonnenbedingten Hautschäden, und deren schwerwiegenderem Gegenstück, dem Plattenepithelkarzinom.
Melanotan-I Wirkungen
Melanotan 1 ursprünglich für die sonnenlose Bräunung entwickelt
MT-1 wurde in klinischen Studien der Phase I auf seine Wirkung auf die Bräunung von Menschen nach UV-Bestrahlung untersucht. Die Studie zeigte, dass Probanden, die MT-1 einnahmen, eine um 75% höhere Wahrscheinlichkeit hatten, braun zu werden, und eine um 47% geringere Wahrscheinlichkeit, zu verbrennen. Im Vergleich zur Kontrollgruppe mussten die Probanden, die Melanotan 1 einnahmen, ihre UV-Belastung um 50% reduzieren, um eine gleichwertige Bräunungswirkung zu erzielen. Außerdem behielten sie ihre Bräune drei Wochen länger bei als diejenigen, die nur UV-Licht ausgesetzt waren. Die Wissenschaftler kamen zu dem Schluss, dass Melanotan 1 zur Förderung der Bräunung in Umgebungen mit hoher UV-Belastung verwendet werden könnte, um die langfristigen Auswirkungen von Sonnenbrand und UV-Hautschäden zu verhindern. Dies ist besonders nützlich für Personen mit bräunenden Hauttypen (nach der Fitzpatrick-Skala als Typ I und Typ II bezeichnet).
Studien an Personen mit der MC1-Rezeptorvariante haben gezeigt, dass sie weniger bräunen als die Allgemeinbevölkerung. Die Verabreichung von Melanotan 1 erhöht in diesen Fällen nachweislich die Melanindichte und die Bräunungswirkung und trägt so zum Schutz von Personen bei, die schlecht bräunen und am dringendsten einen Lichtschutz benötigen. Bei diesen Personen ist der Nutzen von Sonnenschutzmitteln begrenzt, und die Sonnenexposition muss stark eingeschränkt werden, um Hautkrebs zu verhindern. Diese Studie könnte Wege für einen besseren UV-Schutz und eine deutliche Verringerung der Hautkrebsinzidenz eröffnen.
Es besteht auch Interesse an der Verwendung von Melanotan 1 zur Behandlung von Vitiligo. Eine kleine Phase-1-Studie zeigte, dass die Kombination von Melanotan 1 mit UVB-Phototherapie die Melaninproduktion und die Vermehrung der Melanin produzierenden Melanozyten anregte. Fast die Hälfte der behandelten Patienten zeigte eine verbesserte und schnellere Pigmentierung der Vitiligo-Läsionen. Studien haben gezeigt, dass die Kombination von Melanotan 1 mit bestehenden Vitiligo-Behandlungen einen Synergieeffekt haben und die ästhetischen Ergebnisse in kürzerer Zeit verbessern kann. Wenn die Vitiligo-Behandlung erfolgreich ist, kann Melanotan 1 möglicherweise auch zur Behandlung von z. B. hypopigmentierten Narben eingesetzt werden.
Aktinische Keratose, auch als solare Keratose bekannt, ist eine krustige, schuppige Hautveränderung, die durch übermäßige Exposition gegenüber ultraviolettem Licht verursacht wird. Sie gilt als Krebsvorstufe, die unbehandelt schließlich zu einem Plattenepithelkarzinom (einer Form von Hautkrebs) führen kann. Jedes Jahr gibt es mehr als 400.000 Fälle. Obwohl ein Dermatologe oder Chirurg offensichtliche Läsionen entfernen kann, ist die überwiegende Mehrheit von ihnen klein, unsichtbar oder sogar unberührbar.Melanotan 1 wird als mögliches Medikament der ersten Wahl untersucht, um diese unsichtbaren Läsionen zu behandeln und zu verhindern, dass sie sich zu ausgewachsenem Hautkrebs entwickeln.
Melanotan-1-Forschung und Blutdruck
Studien an blutdrucksenkenden Mäusen haben gezeigt, dass Melanotan 1 Bluthochdruck verhindert, ohne Tiere mit normalem Blutdruck zu beeinträchtigen. Dies ist wichtig, da die derzeitigen blutdrucksenkenden Medikamente zu niedrigem Blutdruck führen können, was zu Bewusstlosigkeit, Schlaganfall und Herzinfarkt führen kann. Melanotan 1 ist in der Lage, den Bluthochdruck zu regulieren, ohne eine signifikante Hypotonie zu verursachen, und ist damit ein idealer Kandidat für die Erforschung der weiteren Entwicklung von Medikamenten.
Kognitiver Abbau, Alzheimer-Krankheit und Melanotan 1
Studien an transgenen Mäusen haben gezeigt, dass Melanotan 1 das Gehirn vor Schäden schützt, die zum kognitiven Abbau und zur Alzheimer-Krankheit führen. Die Studie, bei der ein Mausmodell der mittelschweren Alzheimer-Krankheit (AD) verwendet wurde, zeigte, dass Melanotan 1 selbst in sehr geringen Dosen die Menge an Amyloid-Plaques im Gehirn verringerte, die Neuronen vor dem Absterben schützte und die klinischen Messungen der kognitiven Funktion sowie die Labormessungen der synaptischen Übertragung verbesserte. In derselben Studie verhinderte die Blockierung der Wirkung von Melanotan 1 auf den MC4-Rezeptor alle positiven Effekte des Peptids.
In anderen Studien wurde auch der Nutzen von Melanotan 1 auf die Wirkung des MC4-Rezeptors untersucht. Studien, ebenfalls an Mäusen, haben gezeigt, dass die Stimulation des MC4-Rezeptors die Neurogenese fördert und zu einer kognitiven Erholung bei Alzheimer-Patienten führt. Dies ist eine der wenigen Studien, die eine Verbesserung und nicht nur eine Verlangsamung des Abbaus zeigen, und die tägliche Verabreichung von MT-1 senkte die Werte aller mit Alzheimer zusammenhängenden Biomarker, was darauf hindeutet, dass das Peptid tatsächlich über mehrere pathophysiologische Wege wirkt.
Der MC4-Rezeptor ist der einzige Melanocortin-Rezeptor, von dem bekannt ist, dass er auf Astrozyten exprimiert wird, die Neuronen schützen und ernähren. Studien an Ratten haben gezeigt, dass Melanotan 1 die Funktion der Astrozyten verbessert, indem es die Konzentration des neurotrophen Faktors des Gehirns (BDNF) erhöht, der für den Schutz der synaptischen Stabilität und der Neurogenese unerlässlich ist.
Melanotan 1 und funktionelle Erholung nach Schlaganfall
Nicht nur die Biomarker bei Alzheimer verbessern sich nach einer Behandlung mit MT-1. Studien an einem Wüstenrennmausmodell mit zehnminütigem Schlaganfall haben gezeigt, dass die Behandlung mit einer nanomolaren Dosis von Melanotan 2 die Hirnschäden, einschließlich des Absterbens von Neuronen, verringert und die Erholung von Lernen und Gedächtnis verbessert. Besonders spannend ist, dass diese Effekte auch dann erzielt wurden, wenn Melanotan 1 neun Stunden nach dem Schlaganfall verabreicht wurde. Man geht davon aus, dass MT-1 Reparaturmechanismen aktiviert, die die synaptische Plastizität verbessern und eine dauerhafte funktionelle Erholung fördern, indem sie es dem Gehirn ermöglichen, Lernen und Gedächtnis in gesündere Regionen zu verlagern. Der Schlüssel zu diesem Prozess scheint die Expression des Gens Zif268 zu sein, das bei Tieren, denen Melanotan-1 verabreicht wurde, überexprimiert wird. Das gleiche Gen wird auch in einem Modell der Alzheimer-Krankheit überexprimiert, das eine verbesserte kognitive Leistung zeigt.
Melanotan 1 wirkt sich auf Herz und Kreislauf aus
Studien an herzkranken Ratten haben gezeigt, dass Melanotan 1 und andere Melanocortine dazu beitragen, Schäden zu verringern und die Kreislaufparameter zu verbessern. Die Verabreichung von MT-1 während der kardiopulmonalen Wiederbelebung und in Kombination mit Epinephrin trug dazu bei, den arteriellen Ausgangsdruck und die Herzfrequenz wiederherzustellen, die metabolische Azidose umzukehren, Entzündungsmarker zu verringern und die Expression von Genen zu verbessern, die mit der Herzfunktion in Verbindung stehen. Insgesamt verbesserte die Therapie die Überlebensrate um 81%, ein dramatischer Anstieg, der Melanotan 1 oder ähnliche Melanocortine zum Rückgrat der fortgeschrittenen kardialen Notfallhilfe machen könnte.
Melanotan 1 Forschung und neuroinflammatorische Krankheiten
Die Forschung zu Melanotan 1 hat gezeigt, dass der MC1-Rezeptor für die Pigmentierung von Haut und Haaren verantwortlich ist. Lange Zeit ging man davon aus, dass dies die einzige Funktion des Rezeptors ist. Jüngste Studien an Mäusen haben jedoch gezeigt, dass dieser Rezeptor auch bei der Vermittlung von Entzündungen im zentralen Nervensystem eine Rolle spielt. Bei Multipler Sklerose beispielsweise verursachen T-Helferzellen einen neuronalen Myelinmangel, der wiederum zu neuronalen Funktionsstörungen und sogar zum Tod führt. Bei Mäusen greift die Verabreichung von Melanotan 1 in diesen Prozess ein und verhindert den Verlust von Myelin, wodurch neuronale Schäden verhindert werden. Tatsächlich verbesserte die Verabreichung von MT-1 an diese Mäuse die Erholung des Myelins und trug dazu bei, die neuronale Signalübertragung wiederherzustellen.
Ähnliche Wirkungen wie die oben beschriebenen wurden in einem Mausmodell der Uveitis beobachtet, einer entzündlichen Erkrankung des Auges, die zu Schmerzen und zum Verlust des Sehvermögens führen kann. Die derzeitigen Behandlungen haben eine Reihe von Nebenwirkungen, so dass Wissenschaftler ständig nach Alternativen zu Steroiden und immunsuppressiven Medikamenten suchen. alpha-MSH hemmt die Funktion von T-Zellen, eine Eigenschaft, die über den MC4-Rezeptor vermittelt und daher von MT-1 nachgeahmt wird. Überraschenderweise ist die direkte topische Verabreichung von MC4-Rezeptor-Agonisten am Auge ebenso wirksam wie die systemische Verabreichung. Diese Art der Verabreichung trägt dazu bei, systemische Nebenwirkungen zu vermeiden.
Melanotan 1 in Studien zum Fettabbau
Melanotan 1 wirkt auf eine Reihe von Melanocortinrezeptoren, darunter den MC5-Rezeptor, dessen Stimulation die Muskeloxidation von Fettsäuren fördert und die Fettzellen von der Fettspeicherung auf die Fettverbrennung umstellt. Diese Ergebnisse bei Mäusen deuten auch darauf hin, dass die durch Melanocortin-Stimulation ausgelöste Fettverbrennung komplex ist und mehrere Rezeptoren und physiologische Wege involviert.
Referenzierte Zitate
- "Auswirkungen eines superpotenten melanotropen Peptids in Kombination mit solarer UV-Strahlung auf die Bräunung der Haut bei freiwilligen Probanden | Dermatologie | JAMA Dermatology | JAMA Network".
- "Wirkung von MELANOTAN, [Nle(4), D-Phe(7)]-alpha-MSH, auf die Melaninsynthese bei Menschen mit MC1R-Variantenallelen. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16293341. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Afamelanotid und schmalbandige UV-B-Phototherapie zur Behandlung von Vitiligo: eine randomisierte multizentrische Studie". [Online]. Verfügbar: https://reference.medscape.com/medline/abstract/25230094. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Fortschritte bei Vitiligo: An Update on Medical and Surgical Treatments". [Online]. Available: https://reference.medscape.com/medline/abstract/28210378. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "α-MSH-Analogon mildert Blutdruckerhöhung bei DOCA-Salz-hypertensiven Mäusen. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23977363. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Melanocortine schützen vor Hirnschäden und wirken dem kognitiven Abbau in einem transgenen Mausmodell der moderaten Alzheimer׳-Krankheit entgegen. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25034807. [Zugegriffen: 24-https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26003413
- "NDP-α-MSH induziert intensive Neurogenese und kognitive Erholung in Alzheimer-transgenen Mäusen durch Aktivierung von Melanocortin-MC4-Rezeptoren. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar:
- "Melanocortine schützen vor dem Fortschreiten der Alzheimer-Krankheit in dreifach-transgenen Mäusen, indem sie auf mehrere pathophysiologische Pfade abzielen. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24094579. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Der Melanocortin-4-Rezeptor aktiviert den ERK-cFos-Signalweg, um die Expression des hirnabgeleiteten neurotrophen Faktors in Rattenastrozyten und im Hypothalamus zu erhöhen. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25892444. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Funktionelle Erholung nach verzögerter Behandlung des ischämischen Schlaganfalls mit Melanocortinen ist verbunden mit einer Überexpression des aktivitätsabhängigen Gens ... - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19345727. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Schützende Wirkungen des Melanocortin-Analogons NDP-α-MSH bei Ratten, die einen Herzstillstand erlitten haben. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25446929. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Melanocortin-1-Rezeptor-Aktivierung ist neuroprotektiv in Mausmodellen für neuroinflammatorische Erkrankungen. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27797962. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Immunsuppressive Aktivität eines neuen Peptidanalogons des α-Melanozyten-stimulierenden Hormons (α-MSH) bei experimenteller Autoimmun-Uveitis. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21640392. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Periphere Wirkung von Alpha-Melanozyten-stimulierendem Hormon auf die Fettsäureoxidation in der Skelettmuskulatur. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Verfügbar: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17127674. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
- "Charakterisierung von Melanocortin-Rezeptoren bei Mäusen, die die Lipolyse von Adipozyten vermitteln, und Untersuchung der beteiligten Signalwege. - PubMed - NCBI." [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21616121. [Accessed: 24-Jun-2019].
ALLE ARTIKEL UND PRODUKTINFORMATIONEN AUF DIESER WEBSITE DIENEN NUR ZU INFORMATIONS- UND BILDUNGSZWECKEN.
In keiner Weise unterstützt oder befürwortet dieser Arzt/Wissenschaftler den Kauf, den Verkauf oder die Verwendung dieses Produkts aus irgendeinem Grund. MOL Changes hat keine Verbindung oder Beziehung, implizit oder anderweitig, mit diesem Arzt. Der Zweck der Nennung dieses Arztes ist es, die erschöpfende Forschungs- und Entwicklungsarbeit der Wissenschaftler, die an diesem Peptid arbeiten, anzuerkennen, zu würdigen und zu empfehlen.
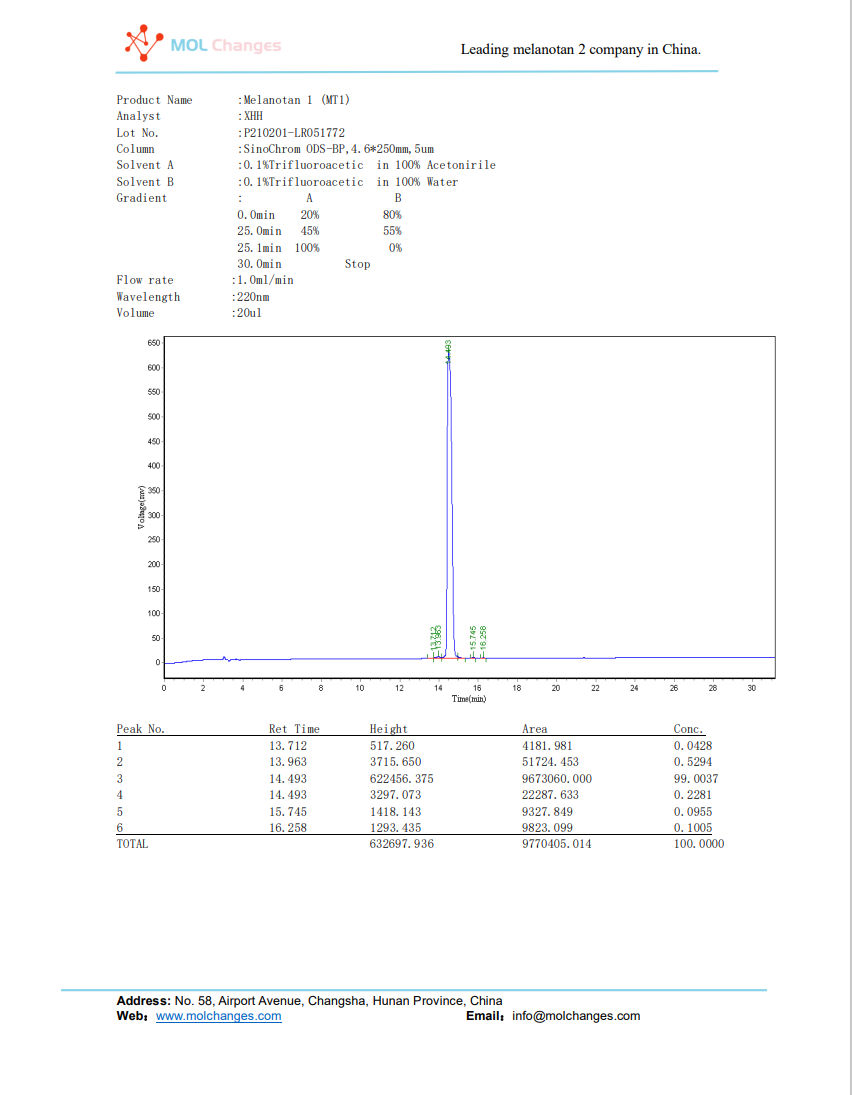
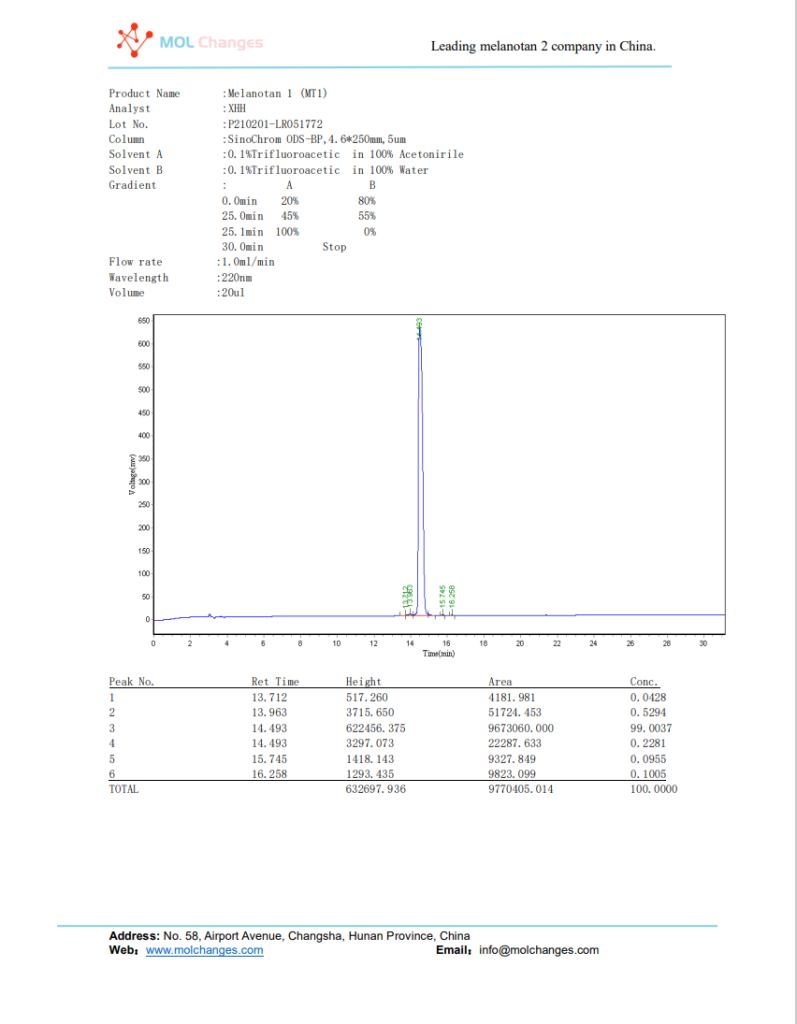
HPLC-Testbericht
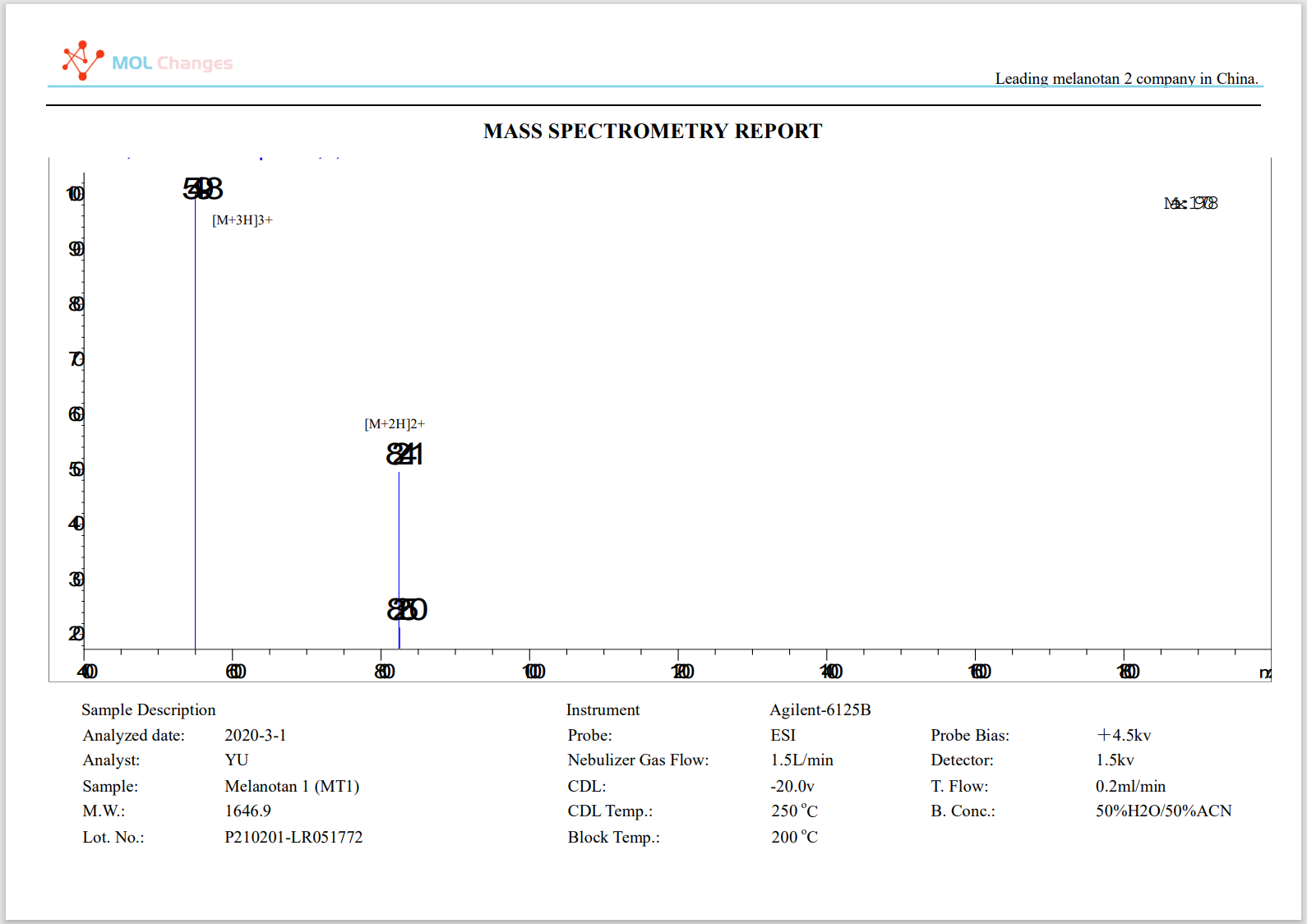
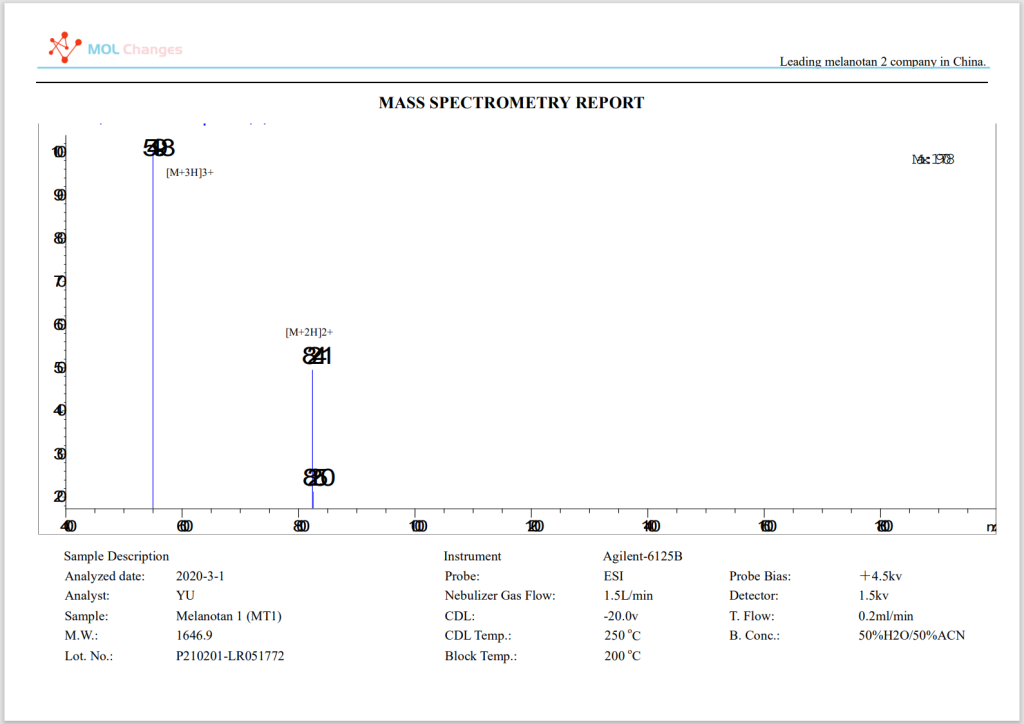
MS-Testbericht
Hersteller-Informationen
- Melanotan-I wird von der Firma MOL Changes hergestellt.
- Melanotan-I-Lieferant MOL Änderungen.
- Höchstzulässige Produktionsmenge: 100000 Flaschen.
- Inhaltsstandard: Netto-Peptid.
- Reinheit: ≥98% für alle Produkte.
- Anpassung: 1mg-1g Größe Anpassung ist akzeptabel