Introduction:
In the quest for effective solutions to combat diabetes, obesity, and weight loss challenges, medical researchers have made significant strides. One such breakthrough is the discovery of tirzepatide, a promising medication that shows immense potential in addressing these health conditions.[1][2]This article presents an original overview of tirzepatide, including its mechanism of action, clinical applications, potential benefits, safety considerations, and future implications.
I. Understanding Tirzepatide's Mechanism of Action
Tirzepatide belongs to a new class of medications known as dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. Its innovative mechanism of action focuses on targeting two crucial hormones involved in glucose regulation and appetite control. By modulating the activity of GIP and GLP-1 receptors, tirzepatide offers a range of clinical applications.
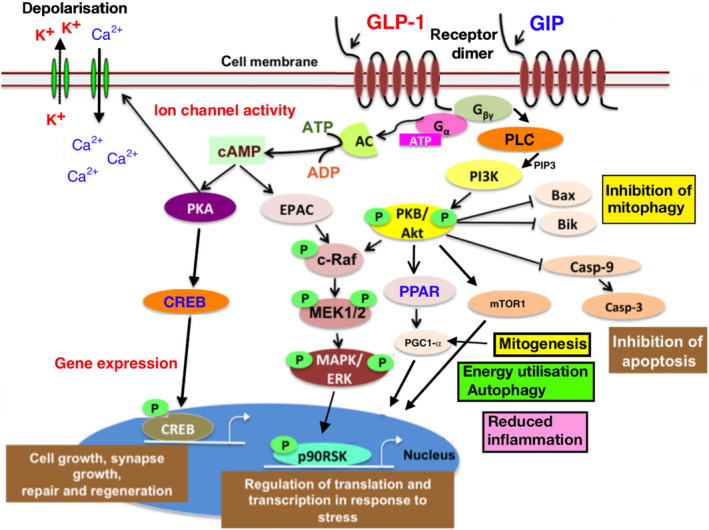
Source: Pubmed
II. Clinical Applications and Benefits
1. Managing Type 2 Diabetes:
Tirzepatide has shown remarkable efficacy in managing type 2 diabetes by improving glycemic control. It stimulates insulin secretion while reducing glucagon release, leading to better regulation of blood glucose levels. Clinical trials have demonstrated significant reductions in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels among patients receiving tirzepatide, surpassing the effects of conventional antidiabetic medications.[3][4]
2. Addressing Obesity and Promoting Weight Loss:
Tirzepatide has also emerged as a potential treatment for obesity and weight loss. Clinical trials have highlighted its capacity to induce substantial weight loss compared to placebos or alternative weight management interventions. The medication’s impact on appetite control, satiety, and energy expenditure contributes to its potential effectiveness in addressing obesity-related challenges.
III. Potential Benefits and Clinical Outcomes
1. Enhanced Glycemic Control:
Tirzepatide’s dual action on GIP and GLP-1 receptors leads to improved glucose regulation, resulting in enhanced glycemic control. By promoting insulin release and suppressing glucagon, tirzepatide helps maintain stable blood glucose levels.
2. Significant Weight Loss:
Clinical studies have demonstrated the remarkable weight loss effects of tirzepatide in individuals with obesity.[1][4] Its influence on appetite regulation and energy balance plays a crucial role in promoting weight reduction and managing body weight.
3. Cardiovascular and Renal Benefits:
Early research suggests that tirzepatide may offer additional cardiovascular and renal benefits beyond glycemic control and weight loss. It shows potential in reducing the risk of cardiovascular events and improving renal function markers. However, further studies are necessary to establish these outcomes conclusively.
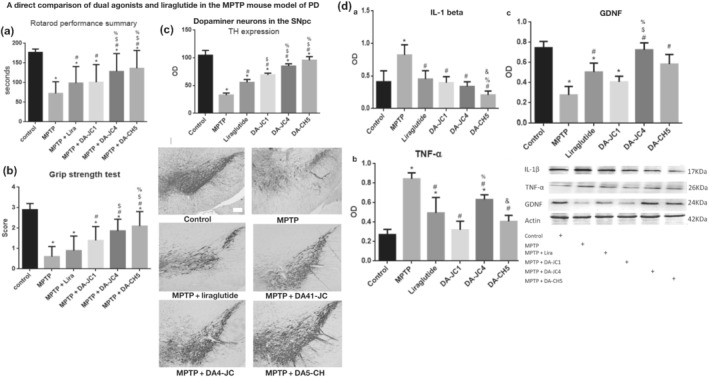
Source: Pubmed
Source: Pubmed
IV. Safety Considerations and Side Effects
While tirzepatide exhibits impressive efficacy, it is essential to consider its safety profile and potential side effects:
1. Gastrointestinal Effects:
The most commonly reported side effects of tirzepatide include mild and transient gastrointestinal discomfort such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. These effects generally diminish with continued use.
2. Hypoglycemia:
Given tirzepatide’s ability to stimulate insulin secretion, there is a risk of hypoglycemia, especially when used in combination with other antidiabetic medications.[2][3][4] Regular blood glucose monitoring and appropriate dosage adjustments can help mitigate this risk.
3. Injection Site Reactions:
Some individuals may experience mild injection site reactions, including redness, itching, or bruising. Adhering to proper injection techniques and rotating injection sites can minimize these effects.
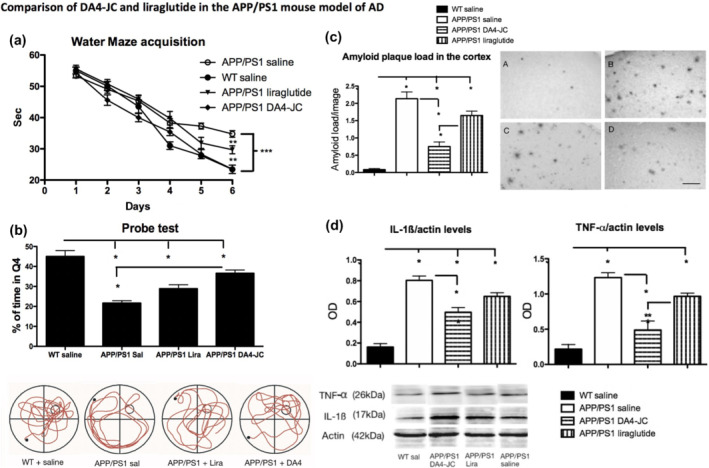
Source: Pubmed
V. Future Implications and Conclusion
Tirzepatide represents a significant advancement in the management of diabetes, obesity, and weight loss.
Author of this article:
Dr. Jean Zeng graduated from king’s college london Faculty of Life Sciences & Medicine.
Scientific Journal paper Author:
Stephen C. Bain
Diabetes Research Group, Swansea University Medical School, Swansea, SA2 8PP, UK
Department of Diabetes and Endocrinology, Singleton Hospital, Swansea Bay University Health Board, Swansea, SA2 8QA, UK.
In no way does this doctor/scientist endorse or advocate the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. MOL Changes.ltd has no affiliation or relationship, implied or otherwise, with this physician. The purpose of citing this doctor is to acknowledge, acknowledge and commend the exhaustive research and development work done by the scientists working on this peptide.
Referenced Citations
[1] Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity
[2] Tirzepatide for wikipedia.
[3] Tirzepatide for Pubmed.
[4] Tirzepatide for drugs.com.

