Peptide modification

The significance of peptide modification: chemical modification is used to maintain or enhance the biological activity of peptides, while optimizing their effective utilization in the body, reducing toxic side effects, prolonging the duration of action, and changing the distribution in the body.
Peptide modification is also an important means of designing peptide drugs. Chemically modified peptides can not only maintain high biological activity, but also effectively avoid the shortcomings of immunogenicity and toxicity. At the same time, chemical modification can give peptides some new excellent properties, providing more reasonable and richer ideas for the development of peptide drugs, including but not limited to C-terminal modification, N-terminal modification, intermediate residue modification, cyclization modification, amidation, acetylation, biotin and FITC labeling, disulfide bond modification, multiple phosphorylation, methylation modification and other methods
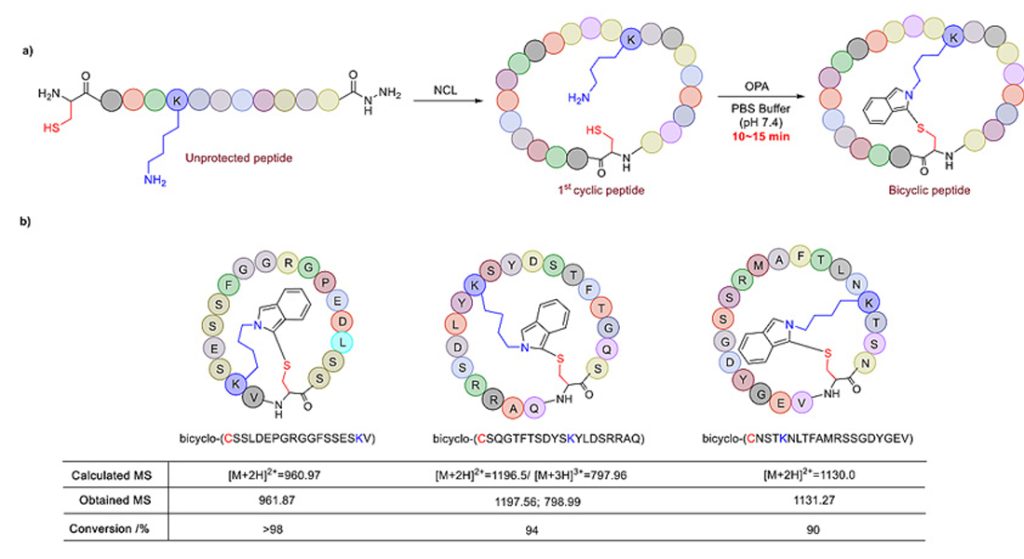
Cyclization
Improving stability and improving membrane permeability can reduce off-target effects and effectively improve drug preparation efficiency and yield.
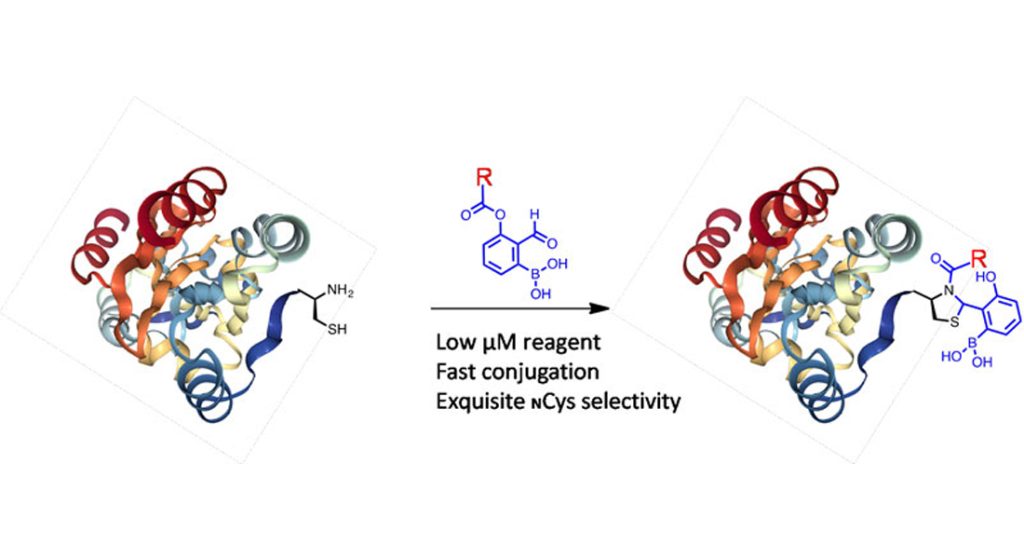
N-terminal
Enhance the stability of peptides, extend the shelf life, eliminate the effect of charge on detection experiments, and improve the biological activity of peptides.
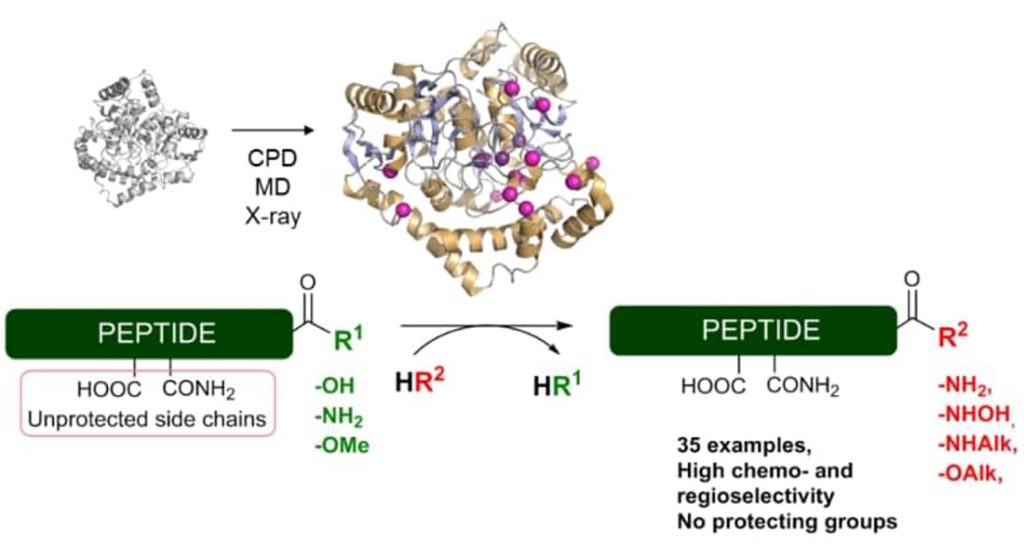
C-terminal
Improving effective utilization in the body can significantly reduce immunogenicity, reduce toxic side effects, increase water solubility, and prolong the action time in the body.
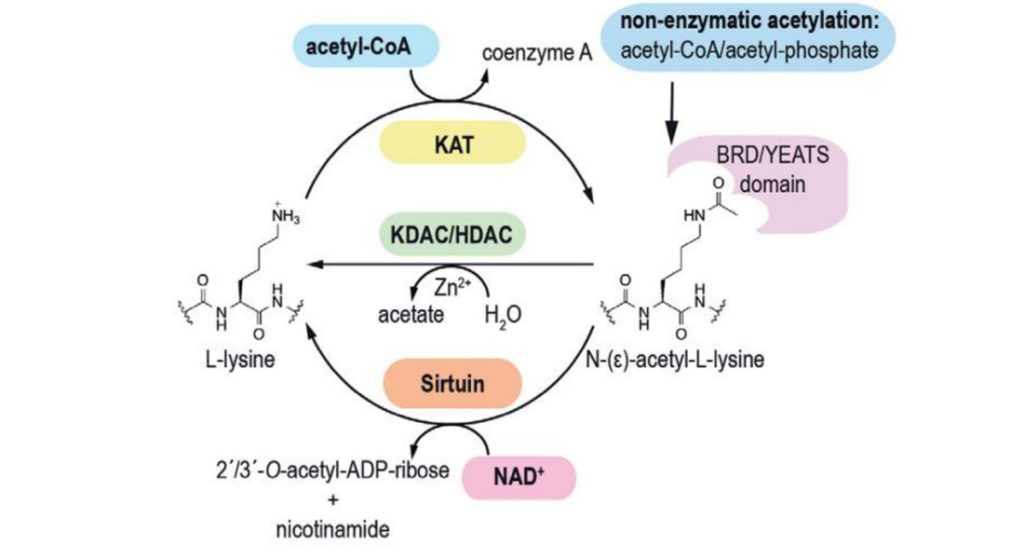
Acetylation
Acetylation technology can not only improve the stability of peptide drugs, but also change the biological activity and pharmacokinetic characteristics of peptides.