MOTS-C
MOTS-c peptide, which stands for mitochondria-derived short open reading frame-c, is a recently discovered bioactive peptide with broad implications for metabolic health.
$4.80 – $16.20
WhatsApp us
◐ Bulk price on WhatsApp!
◐ MOQ: 10 pieces
◐ Peptide manufacturing plant
◐ Implementation of CGMP standards
◐ ISO9001 & ISO14000
SHARE THIS
Product information navigation
MOTS-C Structure
- Sequence:Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Glu-Met-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg
- CAS Number:1627580-64-6
- Molecular Formula:C101H152N28O22S2
- Molecular Weight: 2174.64 g/mol
What is MOTS-C?
The peptide MOTS-c, which stands for Mitochondria-Originally Derived Short Open Reading Frame-c, is a recently discovered biologically active peptide with promising implications for metabolic health.It was first identified in 2015 by a group of researchers studying the effects of exercise on mitochondrial function. It originates from a unique part of the mitochondrial genome called 12S rRNA and is conserved across species, suggesting its evolutionary significance.
MOTS-c has attracted much attention in the scientific community for its multiple regulatory functions on cellular metabolism and its potential therapeutic applications in various metabolic disorders. As a mitochondria-derived peptide, MOTS-c plays a key role in the complex communication network between mitochondria and the nucleus, regulating cellular responses to metabolic stresses and energy demands.
Subsequent studies of MOTS-c have revealed its diverse roles in various cellular processes related to metabolism. It acts as a signaling molecule that regulates gene expression, mitochondrial function, insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. In addition, MOTS-c is involved in adipocyte differentiation, lipid metabolism and control of cellular stress responses.
The discovery of MOTS-c has opened up new avenues of research in mitochondrial biology and metabolic regulation. Scientists are now investigating its potential therapeutic applications in metabolic disorders, obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Although much progress has been made, the full scope of MOTS-c’s mechanism of action and therapeutic potential remains an active area of research that holds great promise for improving human health and addressing the growing global burden of metabolic disease!
MOTS-C Effects
MOTS-c is a 16 amino acid peptide encoded by a mitochondrial gene that plays a crucial role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis throughout the body. Since mitochondria are key sites for ATP production and fatty acid oxidation, the function of MOTS-c is essential for the regulation of metabolic processes.
The body naturally stores fatty acids, amino acids, and glucose to support optimal function. However, metabolic dysfunction may occur when we consume too many calories or live a sedentary lifestyle. This can lead to weight gain and the development of metabolism-related diseases, such as type 2 diabetes.
The ability of MOTS-c to promote metabolic homeostasis makes it a valuable asset for addressing metabolic dysfunction and enhancing metabolic flexibility. However, because it originates from mitochondria, the amount of MOTS-c in the body is dependent on mitochondrial biogenesis, the process by which cells increase the number of mitochondria. Unfortunately, as we age, mitochondrial biogenesis tends to decline, leading to a decrease in MOTS-c production.
To combat age-related MOTS-c decline, peptide therapy can be used, which can increase MOTS-c levels. This can have multiple benefits, including improved metabolic function, enhanced insulin sensitivity, and better management of metabolic-related health conditions.
Here are some of the potential benefits and uses of MOTS-c based on research and preclinical studies:
MOTS-c Promotes Metabolic Health
MOTS-c shows potential effects on metabolism, including improved insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation. It may have implications for managing metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Physical manifestations of MOTS-c
Studies have shown that MOTS-c may enhance physical performance by improving mitochondrial function, increasing energy metabolism and enhancing muscle performance. As a peptide that optimizes mitochondrial function and energy production, MOTS-c may have an impact on muscle growth and performance. Some bodybuilders and athletes hypothesize that MOTS-c may enhance muscle growth and improve athletic performance by promoting fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial biogenesis. This may be beneficial for athletes and individuals seeking to improve athletic performance. As with any new supplement or peptide, it is critical to first purchase a high quality MOTS-c peptide before using it. Peptides. Ltd. offers wholesale peptides as a peptide manufacturer.
MOTS-c Anti-aging
MOTS-c promotes healthy aging by enhancing mitochondrial health and reducing age-related decline. It may help mitigate the effects of aging on various physiological processes and contribute to overall health.
MOTS-c for Cardioprotection
Preliminary studies suggest that MOTS-c peptide may have a protective effect on cardiovascular function. It has been associated with improved endothelial function, reduced cardiac dysfunction and anti-inflammatory effects, suggesting potential benefits for cardiovascular health.
MOTS-c is used in fat metabolism:
MOTS-c appears to regulate fat metabolism by downregulating certain pathways involved in fat storage and promoting β-oxidation (fat burning). This may help to prevent fat accumulation and increase the energy utilization of fat.
MOTS-c Promotes Bone Health
MOTS-c may play a role in promoting osteoblast function and bone formation. It has been associated with improved type I collagen synthesis and osteogenesis, which may contribute to bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
MOTS-c for Insulin Sensitivity and Diabetes
The effect of MOTS-c on insulin sensitivity may be particularly important for thin individuals at risk for insulin resistance and diabetes. It can be used as a monitoring tool and potential intervention to prevent the development of insulin resistance and diabetes.
MOTS-c for neuroprotection
The potential neuroprotective effects of MOTS-c in neurodegenerative diseases have been studied, but more research is needed to fully understand its impact.
MOTS-c for Immunity and Inflammation
The role of MOTS-c in immunity and inflammation is an area of ongoing research, but its potential therapeutic implications in these areas are not yet fully understood.
MOTS-c Side Effects and Safety
As of the most recent available information, no significant adverse side effects have been reported in studies with MOTS-c. Animal studies and in vitro experiments have shown positive results with no apparent toxicity. However, it is important to recognize that further studies are needed to fully evaluate the long-term safety and potential side effects of MOTS-c in humans.
A clinical study by CohBar of a MOTS-c analog called CB4211 in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and obesity demonstrated a well-tolerated and safe profile, with no significant adverse effects reported. These findings are valuable in understanding the safety and potential therapeutic use of MOTS-c analogs.
Because MOTS-c is administered by injection, there may be potential side effects at the injection site, including swelling, irritation, redness, nodules, pain, discomfort, and discoloration. It is important to be aware of these potential risks when considering MOTS-c injections. Purchasing high quality MOTS-c peptides can also help avoid unwanted side effects.
Referenced Citations
- C. Lee, K. H. Kim, and P. Cohen, “MOTS-c: A novel mitochondrial-derived peptide regulating muscle and fat metabolism,” Free Radic. Biol. Med., vol. 100, pp. 182–187, Nov. 2016. [PMC]
- H. Lu et al., “MOTS-c peptide regulates adipose homeostasis to prevent ovariectomy-induced metabolic dysfunction,” J. Mol. Med. Berl. Ger., vol. 97, no. 4, pp. 473–485, Apr. 2019. [PubMed]
- K. H. Kim, J. M. Son, B. A. Benayoun, and C. Lee, “The Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c Translocates to the Nucleus to Regulate Nuclear Gene Expression in Response to Metabolic Stress,” Cell Metab., vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 516-524.e7, Sep. 2018. [PMC]
- S.-J. Kim et al., “The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c is a regulator of plasma metabolites and enhances insulin sensitivity,” Physiol. Rep., vol. 7, no. 13, p. e14171, Jul. 2019. [PubMed]
- R. Crescenzo, F. Bianco, A. Mazzoli, A. Giacco, G. Liverini, and S. Iossa, “A possible link between hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction and diet-induced insulin resistance,” Eur. J. Nutr., vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 1–6, Feb. 2016. [BMJ]
- L. R. Cataldo, R. Fernández-Verdejo, J. L. Santos, and J. E. Galgani, “Plasma MOTS-c levels are associated with insulin sensitivity in lean but not in obese individuals,” J. Investig. Med., vol. 66, no. 6, pp. 1019–1022, Aug. 2018. [PubMed]
- N. Che et al., “MOTS-c improves osteoporosis by promoting the synthesis of type I collagen in osteoblasts via TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway,” Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci., vol. 23, no. 8, pp. 3183–3189, Apr. 2019. [PubMed]
- B.-T. Hu and W.-Z. Chen, “MOTS-c improves osteoporosis by promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via TGF-β/Smad pathway,” Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci., vol. 22, no. 21, pp. 7156–7163, Nov. 2018. [PubMed]
- N. Fuku et al., “The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c: A player in exceptional longevity?,” Aging Cell, vol. 14, Aug. 2015. [Research Gate]
- Q. Qin et al., “Downregulation of circulating MOTS-c levels in patients with coronary endothelial dysfunction,” Int. J. Cardiol., vol. 254, pp. 23–27, 01 2018. [PubMed]
- Y. Yang et al., “The role of mitochondria-derived peptides in cardiovascular disease: Recent updates,” Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomedecine Pharmacother., vol. 117, p. 109075, Jun. 2019. [PubMed]
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
In no way does this doctor/scientist endorse or advocate the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. MOL Changes has no affiliation or relationship, implied or otherwise, with this physician. The purpose of citing this doctor is to acknowledge, acknowledge and commend the exhaustive research and development work done by the scientists working on this peptide.
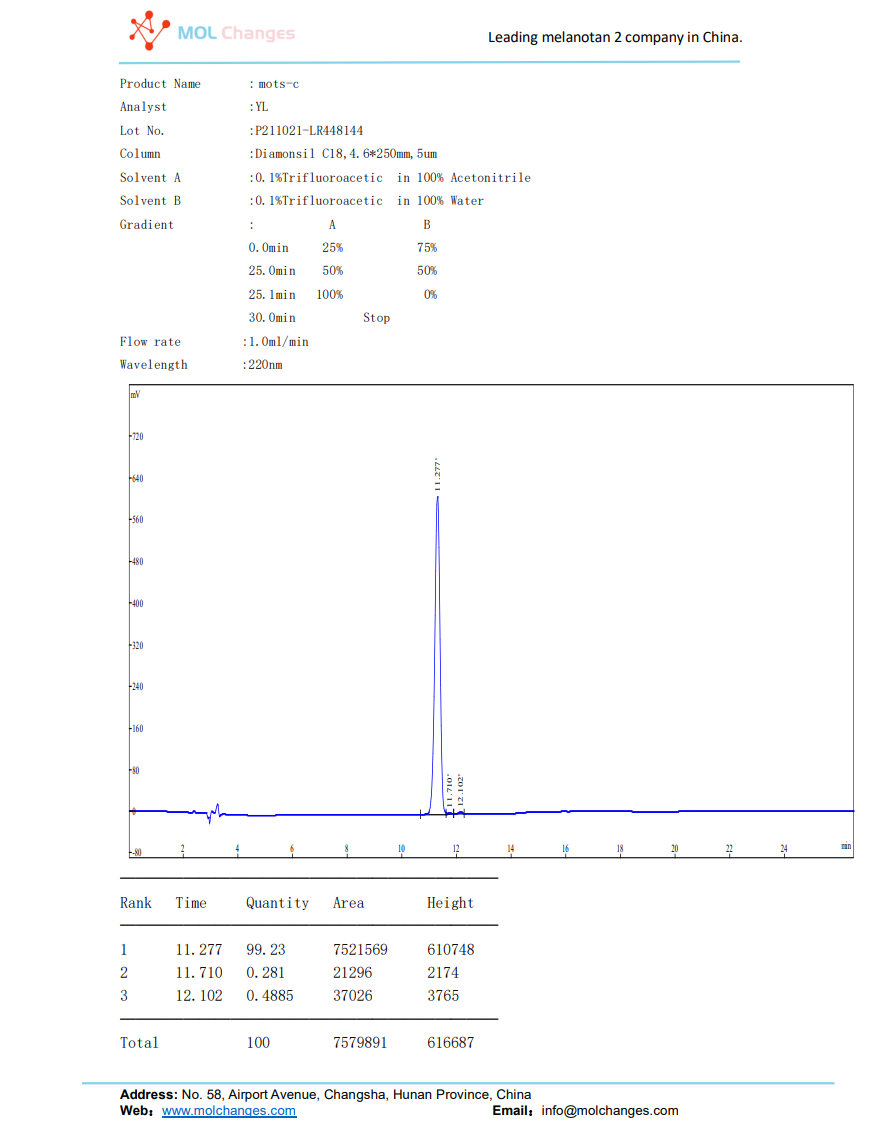
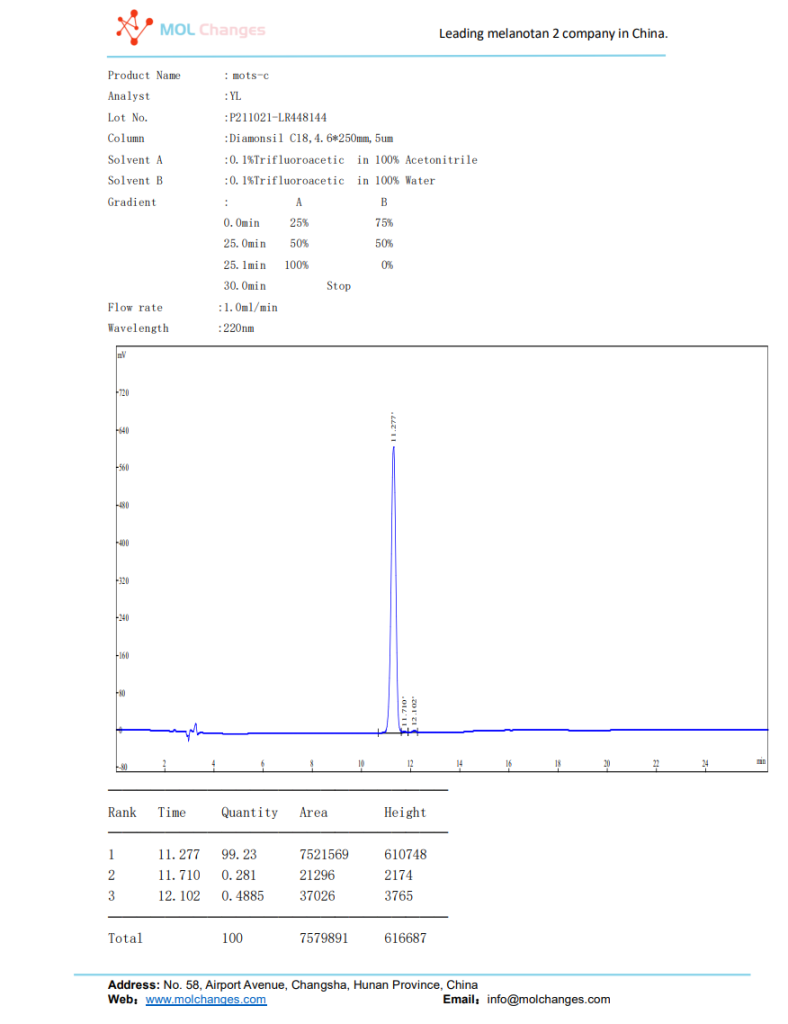
HPLC test report
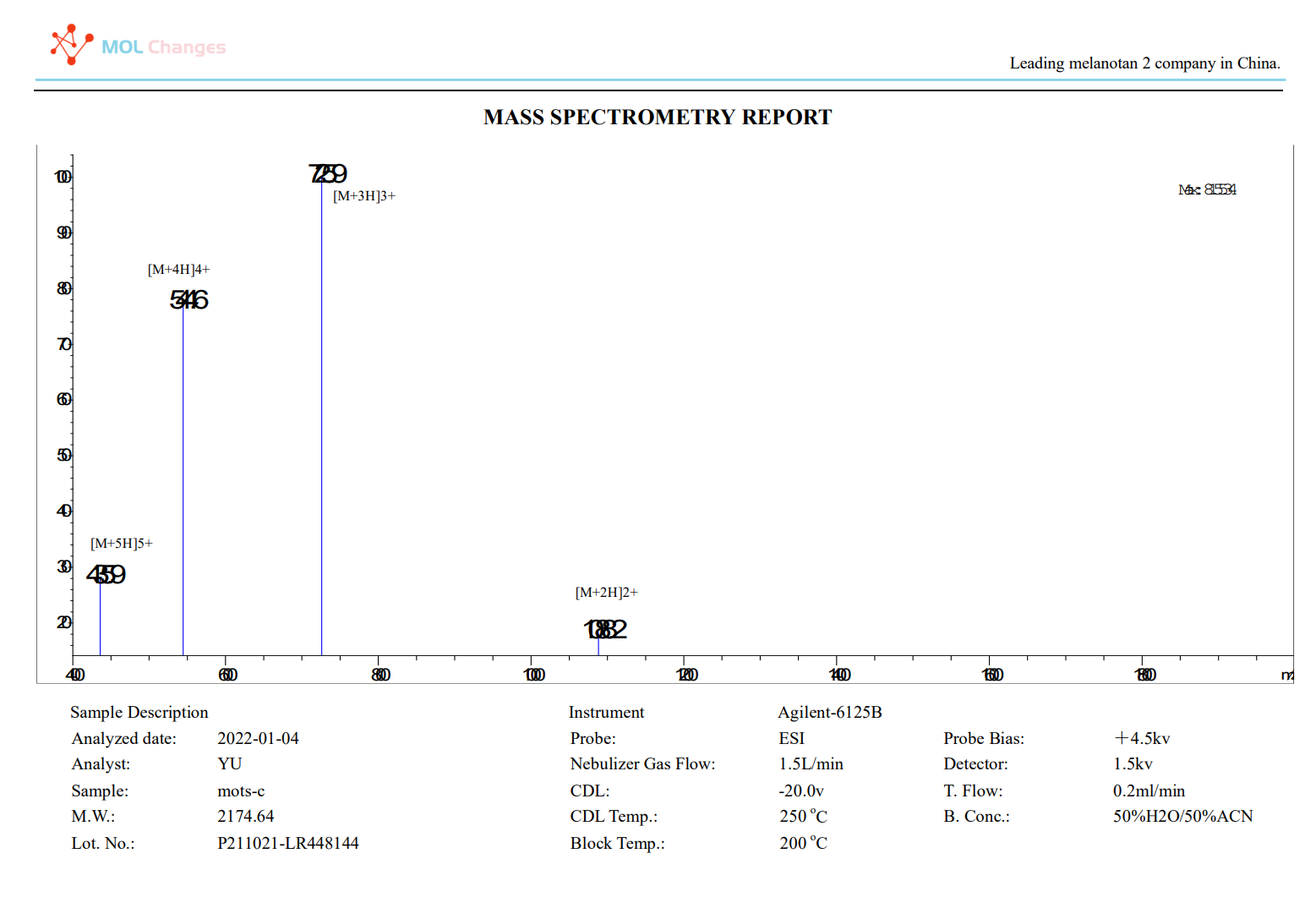
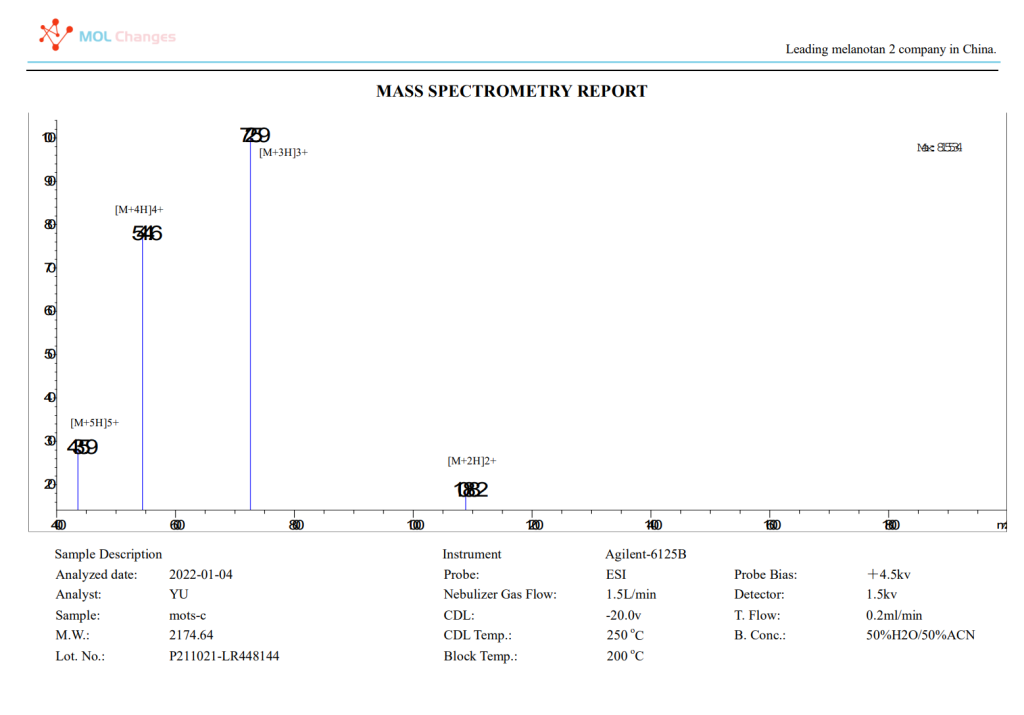
MS test report
Manufacturer Information
- MOTS-C is manufactured by MOL Changes factory.
- MOTS-C supplier MOL Changes.
- Maximum acceptable production volume: 100000 bottles.
- Content standard: net peptide.
- Purity: ≥98% for all products.
- Customization: 1mg-1g size customization is acceptable