多肽修饰
多肽聚乙二醇化
什么是多肽 Pegylation?
肽聚乙二醇化是将一条或多条聚乙二醇(PEG)链共价连接到肽分子上的过程。聚乙二醇化可以增加肽的分子量,保护肽不被蛋白水解酶水解,并最终改善肽的药代动力学。
肽在制药业和药物治疗开发中发挥着重要作用。然而,由于蛋白水解酶的快速降解、溶解性差、抗原反应以及肾小球滤过等原因,多肽在体内的应用受到了限制。聚乙二醇(PEG)共价连接可降低免疫原性、提高溶解度并减少肾脏清除率。添加单分散 PEG 链是 PEG 化肽治疗开发的关键因素。这些安全有效的聚乙二醇化肽对获得最佳疗效至关重要。

多肽 Pegylation 科学家
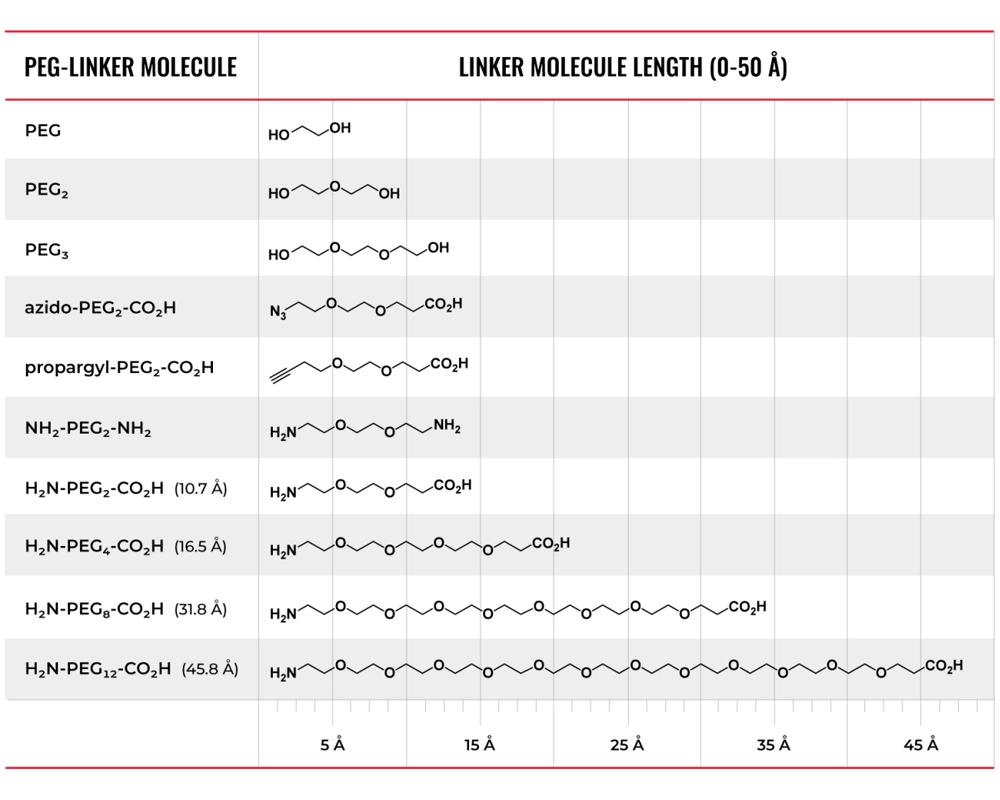
常见 PEG 连接器和缩写
-点击化学反应,在 PEG 试剂的叠氮基团和肽的炔基团之间发生化学反应,反之亦然。
-Suzuki-Miyaura偶联,发生在 PEG 试剂的碘苯基和肽的芳基硼酸基之间,反之亦然。
-Sonogashira偶联,发生在 PEG 试剂的碘苯基和肽的炔基之间,反之亦然。
|
缩写
|
全 PEG 链名称
|
|---|---|
|
PEG |
四甘醇 |
|
小型 PEG2 |
8-氨基-3,6-二氧杂辛酸 |
|
微型 PEG3 |
氨基-3,6,9-三氧杂十一烷酸 |
|
NH2-PEG2- 酸 |
3-(2-(2-氨基乙氧基)乙氧基)丙酸 |
|
PEG750 |
聚乙二醇甲醚(平均锰含量 750 |
|
PEG1000 |
聚乙二醇甲醚(平均锰含量 1000 |
|
PEG2000 |
聚乙二醇甲醚(平均 Mn 2000 |
|
PEG5000 |
聚乙二醇甲醚(平均 Mn 5000 |
|
酯 (OTBzl) |
对硝基苯胺 |
|
KLH(C 端的-COOH) |
tBu |
特色引文
开发用于血管内皮生长因子 PET 成像的放射性标记不可逆多肽配体
Imaging agents based on peptide probes have desirable pharmacokinetic properties provided that they have high affinities for their target in vivo. An approach to improve a peptide ligand’s affinity for its target is to make this interaction covalent and irreversible. For this purpose, we evaluated a 64Cu-labeled affinity peptide tag, 64Cu-L19K-(5-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene) (64Cu-L19K-FDNB), which binds covalently and irreversibly to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a PET imaging agent. We compared the in vivo properties of 64Cu-L19K-FDNB in VEGF-expressing tumor xenografts with its noncovalent binding analogs, 64Cu-L19K-(2,4-dinitrophenyl) (64Cu-L19K-DNP) and 64Cu-L19K. Methods: The L19K peptide (GGNECDIARMWEWECFERK-CONH2) was constructed with 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid at the N terminus for radiolabeling with 64Cu with a polyethylene glycol spacer between peptide and chelate. 1,5-difluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene was conjugated at the C-terminal lysine for cross-linking to VEGF, resulting in L19K-FDNB. 64Cu-L19K-FDNB was assayed for covalent binding to VEGF in vitro. As a control, L19K was conjugated to 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, resulting in L19K-DNP. PET imaging and biodistribution studies of 64Cu-L19K-FDNB, 64Cu-L19K-DNP, and the native 64Cu-L19K were compared in HCT-116 xenografts. Blocking studies of 64Cu-L19K-FDNB was performed with a coinjection of excess unlabeled L19K-FDNB. Results: In vitro binding studies confirmed the covalent and irreversible binding of 64Cu-L19K-FDNB to VEGF, whereas 64Cu-L19K-DNP and 64Cu-L19K did not bind covalently. PET imaging showed higher tumor uptake with 64Cu-L19K-FDNB than with 64Cu-L19K-DNP and 64Cu-L19K, with mean standardized uptake values of 0.62 ± 0.05, 0.18 ± 0.06, and 0.34 ± 0.14, respectively, at 24 h after injection (P < 0.05), and 0.53 ± 0.05, 0.32 ± 0.14, and 0.30 ± 0.09, respectively, at 48 h after injection (P < 0.05). Blocking studies with 64Cu-L19K-FDNB in the presence of excess unlabeled peptide showed a 53% reduction in tumor uptake at 48 h after injection. Conclusion: In this proof-of-concept study, the use of a covalent binding peptide ligand against VEGF improves tracer accumulation at the tumor site in vivo, compared with its noncovalent binding peptide analogs. This technique is a promising tool to enhance the potency of peptide probes as imaging agents.
肽修饰
在多肽修饰方面经验丰富,为多肽研究提供了多种可行的途径。
