Peptide Modifications
Peptide Glycosylation
What is peptide glycosylation?
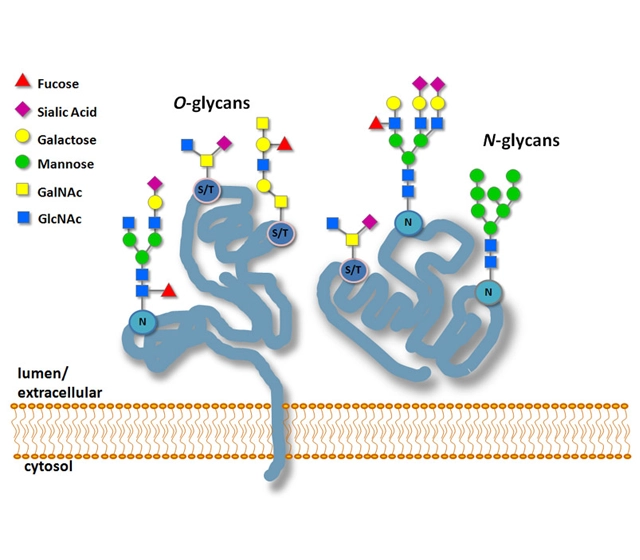
Peptide glycosylation is the covalent attachment of carbohydrate molecules (glycans) to peptides or proteins to form glycopeptides or glycoproteins. This process takes place mainly through:
N-linked glycosylation: the glycan is bound to an asparagine (Asn) residue with the sequence Asn-X-Ser/Thr (X≠Pro).
O-linked glycosylation: the glycan is attached to a serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residue.
Function: Enhances protein stability, aids in proper folding, facilitates intercellular communication, and plays a role in immune responses and disease mechanisms (e.g., cancer biomarkers).
It is commonly found in eukaryotes and some bacteria and is essential for biological processes and biopharmaceutical applications such as antibody drugs.
Common Glycosylated Amino Acids
linkage glycosylation
N-linked glycosylation is more common and O-linked glycosylation is more varied, usually occurring on the side chains of Ser, Thr and/or Asn, but other amino acids can also be glycosylated.
Sugar |
Amino Acid |
Glycated Amino Acid |
|---|---|---|
|
α-D-Galactose |
Serine |
Ser(alpha-D-GalNAc) |
|
α-D-Galactose |
Threonine |
Thr(alpha-D-GalNAc) |
|
β-D-Galactose |
Serine |
Ser(beta-D-GalNAc) |
|
β-D-Galactose |
Threonine |
Thr(beta-D-GalNAc) |
|
β-D-Galactose |
Serine |
Ser(Gal-beta(1-3)GalNAc) |
|
β-D-Glucose |
Serine |
Ser(beta-D-GlcNAc) |
|
β-D-Glucose |
Threonine |
Thr(beta-D-GlcNAc) |
|
β-D-Glucose |
Asparagine |
Asn(beta-D-GlcNAc) |
|
β-D-Glucose |
Serine |
Ser(beta-D-Glc) |
|
α-D-Mannose |
Serine |
Thr(alpha-D-Man) |
|
α-D-Mannose |
Asparagine |
Asn(alpha-D-Man) |
|
α-D-Mannose |
Serine |
Ser(alpha-D-Man) |
|
α-D-Mannose |
Threonine |
Thr(alpha-D-Man) |
Featured Citations
Preparation and preliminary biological evaluation of n-Gluc-Lys([Al18 F]NOTA)-TOCA
Octreotide and their derivatives can specificially bind with somatostatin receptor (SSTR) which is usually over-expressed on many tumor cells. So 18F labeled octreotide and their derivatives can be used for the diagnosis and evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of SSTR positive tumors. In order to explore a novel PET probe for diagnosis of SSTR positive tumors, the n-Gluc-Lys([Al18F]NOTA)-TOCA was radio-synthesized fast and efficiently using the chelation reaction of n-Gluc-Lys(NOTA)-TOCA with Al18F moiety, n-Gluc-Lys([Al18F]NOTA)-TOCA was a glycosylated octreotide derivative combined with 1, 4, 7-triazacyclononane-1, 4, 7-triacetic acid(NOTA). The labeling efficiency of n-Gluc-Lys([Al18F]NOTA)-TOCA is 69% and the total synthesis time is 25-30 min. The radiochemical purity is over 95% after HLB column purification. The stability in vitro is excellent, and the hydrophilicity is high (lg P = -4.20 ± 0.09(n = 3)). Biodistribution studies in normal mice at 2 h after injection show that the uptake of n-Gluc-Lys([Al18F]NOTA)-TOCA in kidney is high ((13.83 ± 3.52)% ID/g(n = 5)) and the uptake in liver and bone is low. The uptake in samatostatin pancreas receptor express is high, and the background of blood and muscle is low. These preliminary results provide some experimental basis for further study of Al18F complex labeled octreotide and their analogues as tumor probes for the diagnosis of SSTR-positire tumors. (authors)
Related Peptide Modification Services
peptide glycosylation
peptide glycosylation
Peptide glycosylation is a covalent modification that can potentially improve the physicochemical properties of peptides
Read Morepeptide Phosphorylation
peptide Phosphorylation
Phosphoralation may occur on Serine (S, Ser), Threonine (T, Thr) and Tyrosine (Y, Tyr) side chains by phosphoester bond formation
Read MoreStapled Peptides
Stapled Peptides
Introduction of two unnatural amino acids containing α-methyl, α-alkenyl groups during solid-phase synthesis of peptide chains.
Read MoreCyclic Peptide
Cyclic Peptide
Peptide cyclisation enhances the conformational stability of peptides (relative to their linear analogues) and is a common strategy in peptide development.
Read Morepeptide modification
Extensive experience in peptide modification, providing multiple viable avenues for peptide research.