Peptide Modifications
C-terminal modification
What is C-terminal modification?
C-terminal modifications play a crucial role in peptide chemistry, enabling researchers to tailor peptide function to a variety of scientific and pharmaceutical applications. These modifications primarily affect peptide stability, charge, binding affinity and biological activity.The MOL Changes team offers a wide range of C-terminal modification services to provide researchers with highly customised peptides for research and therapeutic use.
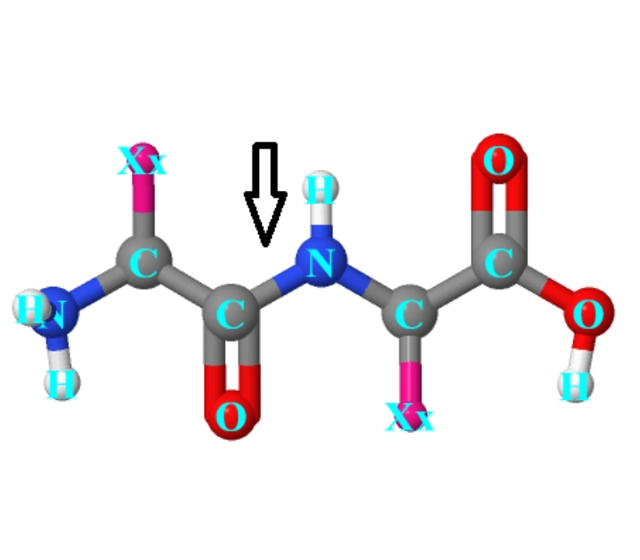
Common C-terminal modifications
Modification type
MOL Changes offers a variety of C-terminal modification options to help scientists choose the best chemical structure for their specific research goals.
AFC |
MAPS Asymmetric 2 branches |
CMK |
|---|---|---|
|
AMC |
MAPS Asymmetric 4 branches |
Lys(Biotin) |
|
Amidation |
MAPS Asymmetric 8 branches |
Lys(5-FAM) |
|
BSA (-COOH of C terminal) |
Me |
Lys(TMR) |
|
Bzl |
NHEt |
Lys(Dansyl) |
|
Cysteamide |
NHisopen |
DABCYL/Glu-NH2 |
|
Ester (OEt) |
NHMe |
|
|
Ester (OMe) |
OSU |
|
|
Ester (OtBu) |
OVA (-COOH of C terminal) |
|
|
Ester (OTBzl) |
p-Nitroanilide |
|
|
KLH (-COOH of C terminal) |
tBu |
Featured Citations
C-Terminal Peptide Modifications Reveal Direct and Indirect Roles of Hedgehog Morphogen Cholesteroylation
Hedgehog (Hh) morphogens are involved in embryonic development and stem cell biology and, if misregulated, can contribute to cancer. One important post-translational modification with profound impact on Hh biofunction is its C-terminal cholesteroylation during biosynthesis. The current hypothesis is that the cholesterol moiety is a decisive factor in Hh association with the outer plasma membrane leaflet of producing cells, cell-surface Hh multimerization, and its transport and signaling. Yet, it is not decided whether the cholesterol moiety is directly involved in all of these processes, because their functional interdependency raises the alternative possibility that the cholesterol initiates early processes directly and that these processes can then steer later stages of Hh signaling independent of the lipid. We generated variants of the C-terminal Hh peptide and observed that these cholesteroylated peptides variably impaired several post-translational processes in producing cells and Hh biofunction in Drosophila melanogaster eye and wing development. We also found that substantial Hh amounts separated from cholesteroylated peptide tags in vitro and in vivo and that tagged and untagged Hh variants lacking their C-cholesterol moieties remained bioactive. Our approach thus confirms that Hh cholesteroylation is essential during the early steps of Hh production and maturation but also suggests that it is dispensable for Hh signal reception at receiving cells.
Related Peptide Modification Services
peptide glycosylation
peptide glycosylation
Peptide glycosylation is a covalent modification that can potentially improve the physicochemical properties of peptides
Read Morepeptide Phosphorylation
peptide Phosphorylation
Phosphoralation may occur on Serine (S, Ser), Threonine (T, Thr) and Tyrosine (Y, Tyr) side chains by phosphoester bond formation
Read MoreStapled Peptides
Stapled Peptides
Introduction of two unnatural amino acids containing α-methyl, α-alkenyl groups during solid-phase synthesis of peptide chains.
Read MoreCyclic Peptide
Cyclic Peptide
Peptide cyclisation enhances the conformational stability of peptides (relative to their linear analogues) and is a common strategy in peptide development.
Read Morepeptide modification
Extensive experience in peptide modification, providing multiple viable avenues for peptide research.